World distribution of volcanoes
A volcano is a conical hill or mountain which transfers molten rock known as magma from depth to the Earth's surface. On Earth, volcanoes are generally found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging. The word volcano is derived from Vulcan, the name of a god of fire in Roman mythology.
This visual offers a glimpse of the world’s volcanoes, all active, dormant and extinct volcanoes. It elaborates the distribution of volcanoes in relation to tectonic plate boundaries. Other surface details have been nullified here to highlight the distributional pattern of world volcanoes and associated details like extent of individual plates over continent and ocean. The symbology used helps to easily identify the Ring of Fire in the basin of the Pacific Ocean.
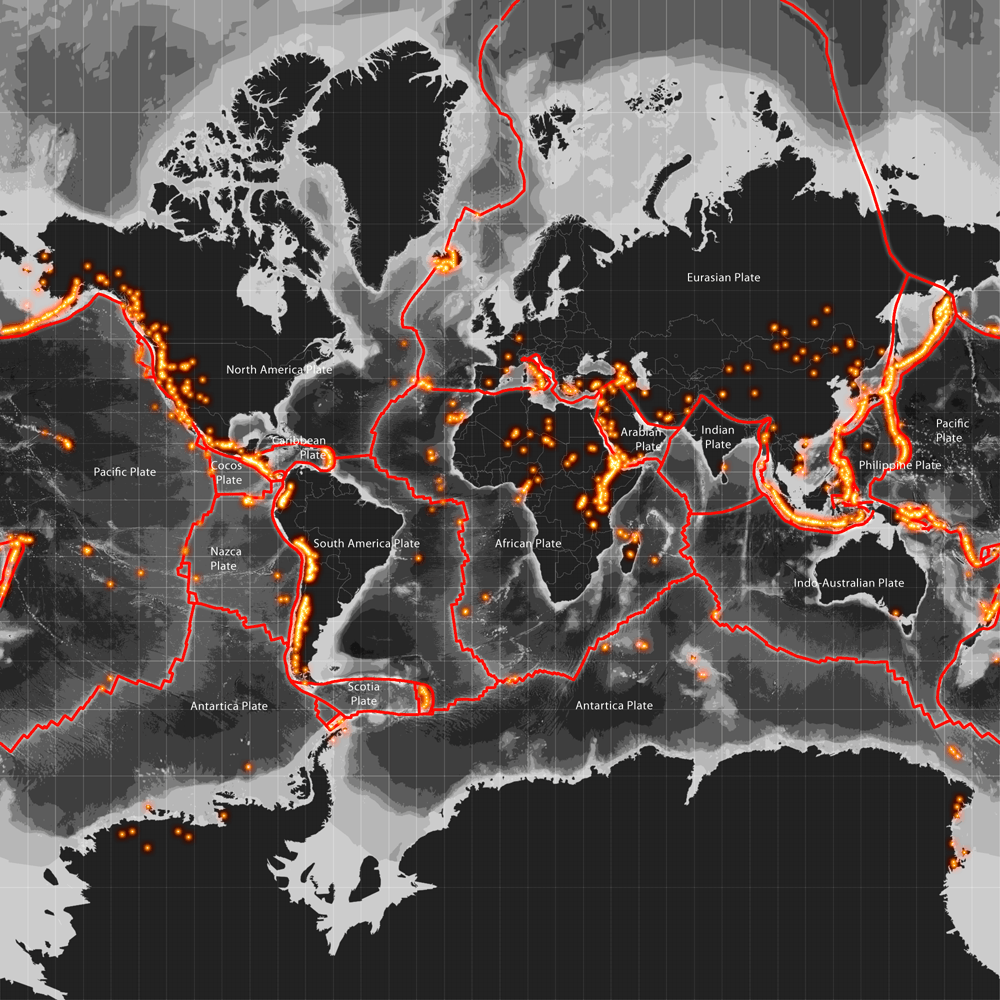
Data source: Global Volcanism Program (GVP)



